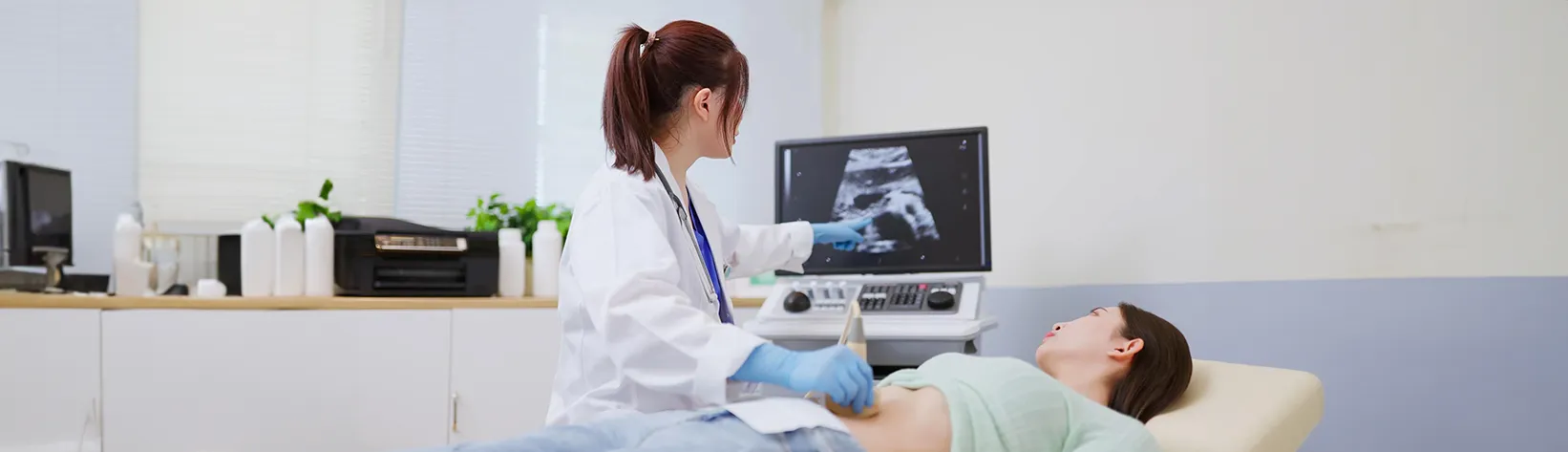
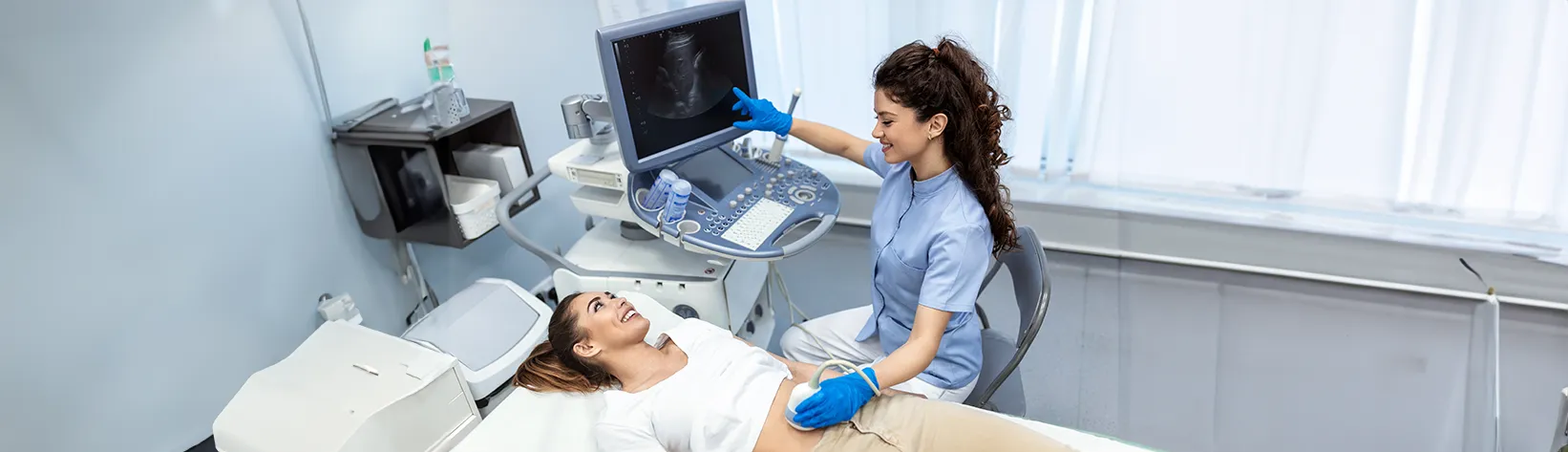
The medical imaging method known as ultrasound scans makes use of high-frequency sound waves in order to create real-time images of the inside of the body. Ultrasound is commonly used to visualise organs such as the liver, kidneys, uterus, and foetus during pregnancy, as well as to assess blood flow in vessels.
Ultrasound is a safe, painless and non-invasive diagnostic imaging method because it does not involve exposure to ionising radiation like X-rays or CT scans do.
In this article, we’ll discuss how ultrasound scans work, their types as well as the many advantages they provide for medical diagnosis and treatment.
Principles Behind Ultrasound
Modern medical diagnostics rely heavily on ultrasound scans, which are based on the complex laws of sound wave propagation in the human body. Through the use of a specialised instrument called a transducer, high-frequency sound waves are harnessed for these scans.
This radiation interacts with the various tissues that are found inside the body to produce echoes, which are then recorded and processed to create finely detailed images.
Ultrasound Machine Components
An ultrasonic machine generally consists of several essential parts, each carefully designed to perform a particular function during the imaging process.
The transducer is the primary source of sound waves among these parts, making it the most important one. Furthermore, these waves are captured, processed, and translated into coherent visual images by advanced processors and display units working together.
A coupling gel is used to provide the best possible sound wave transmission and reception, guaranteeing precise and fluid imaging results. When combined, these elements create a seamless system that gives medical professionals priceless insights into the workings of the human body.
Process of Ultrasound Imaging
A number of planning stages and procedural considerations are involved in the ultrasound scan process to guarantee the best possible imaging outcomes. Patients might be expected to follow specific pre-scan instructions, such as fasting or drinking certain fluids, before the scan starts.
By reducing interference from outside sources, these techniques help to maximise the clarity and accuracy of the final images. The actual scanning process begins after the preparatory stage is finished.
Patient comfort and safety are given utmost priority during this process, and medical professionals use various techniques to guarantee a smooth and anxiety-free experience for the patient.
Types of Ultrasound Scans
There are three types of ultrasound scans:
2D Ultrasound
The most popular type of ultrasound produces two-dimensional images of the scanned area. It is frequently used in gynaecology and obstetrics to track the growth of the unborn child during pregnancy.
3D Ultrasound
3D ultrasound offers three-dimensional images, providing more detailed visualisation of organs and structures. It is important in assessing foetal abnormalities and guiding specific medical procedures.
4D Ultrasound
4D ultrasound adds the element of time, allowing real-time visualisation of fetal movements. This advancement enhances the bonding experience for expectant parents and facilitates comprehensive foetal assessment.
Benefits of Ultrasound Scans
Ultrasound scans offer several benefits in medical diagnosis and treatment. Here are a few benefits of ultrasound scans:
Non-Invasive
Ultrasound scans are non-invasive, so there is little chance of discomfort or danger for the patient during the process. Ultrasound exams don’t require any incisions or needles, which makes them less intrusive than invasive procedures like surgery or biopsies. It helps in guaranteeing patient safety and comfort.
Real-Time Imaging
One of the ultrasound’s most significant benefits is that it can provide real-time imaging, which enables medical professionals to watch the dynamic movement and function of tissues and organs as they happen.
When it comes to guiding surgeries, monitoring foetal development during pregnancy, or evaluating the health of organs such as the heart or blood vessels, this dynamic imaging capability is precious.
No Radiation Exposure
Ultrasound does not use ionising radiation to create images, in contrast to CT and X-ray scans. This feature removes concerns about cumulative radiation exposure over time and makes ultrasound safer for patients, including pregnant women and those in need of frequent imaging studies.
Cost-Effective
Compared to other types of imaging, like CT or MRI scanners, ultrasound machines are usually more affordable, lightweight, and portable. Because of its portability, ultrasound can be used in a variety of healthcare settings, such as emergency rooms, remote or underserved regions, and even at patients’ bedsides.
Early Detection and Intervention
Patient outcomes are significantly impacted by ultrasound’s ability to identify abnormalities early on and enable timely intervention and treatment. It is imperative for several other medical specialities to diagnose and treat different conditions and for obstetrics to monitor foetal development and detect congenital disabilities.
Conclusion
Ultrasound scans provide information about the inner workings of the human body, making them essential to modern medical diagnostics. These scans provide doctors with non-invasive, real-time images to help with the diagnosis and monitoring of a variety of medical conditions by using high-frequency sound waves.