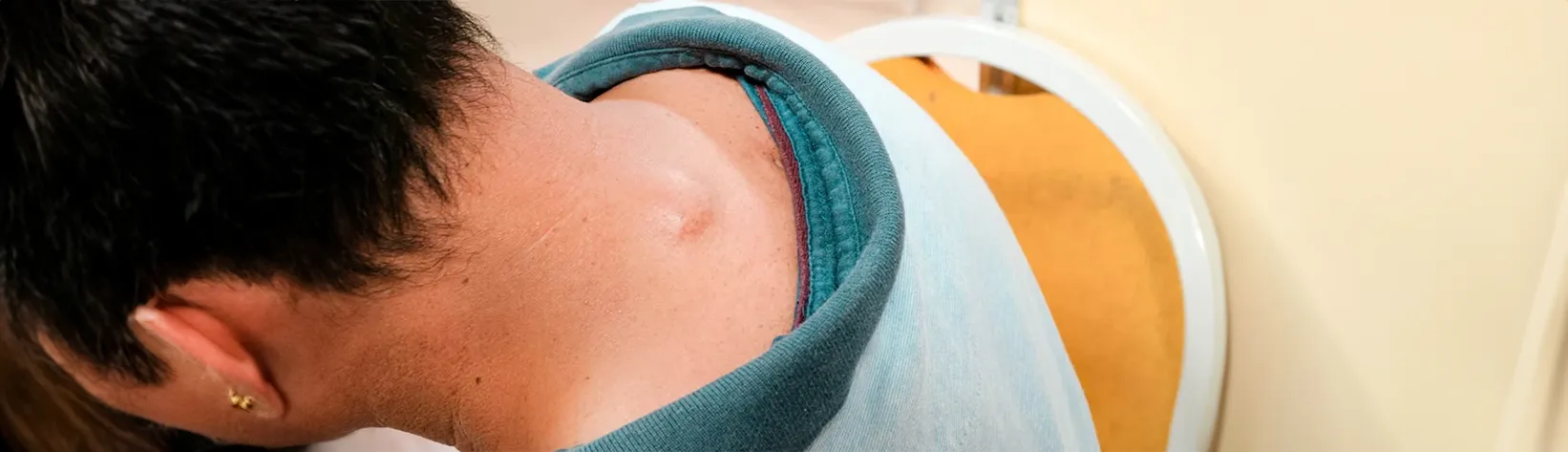
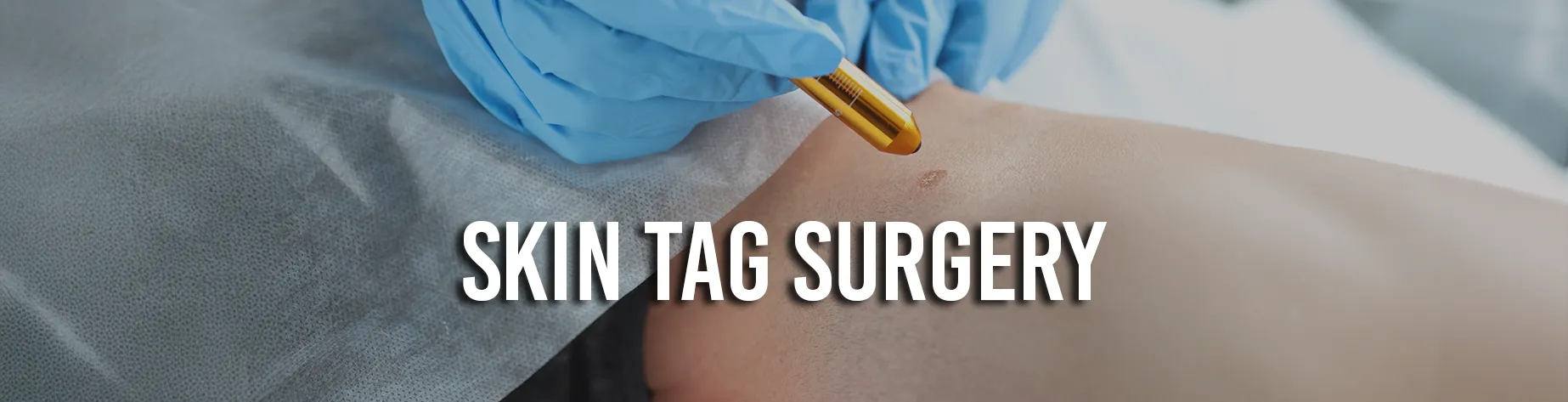
Sebaceous cysts are common benign skin infections that affect individuals of all ages. These cysts develop when the sebaceous glands, the organs responsible for creating oil to moisturise the skin and hair, get infected or injured.
Sebaceous cysts can pop up anywhere on the body, but the face, scalp, back, ears, trunk and groin area are the body parts where they are commonly formed.
Even though sebaceous cysts are typically benign, people may experience discomfort and stress because of them. For efficient management and mental peace, it is vital to understand their causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Sebaceous Cysts
Sebaceous cysts are small, noncancerous lumps that form beneath the skin. They begin to appear when the skin’s oil-producing glands become clogged. Keratin, the protein that makes up hair and nails, is usually found inside these cysts and has a yellowish, cheesy consistency. Inflammation and swelling can occasionally result from sebaceous cysts, even though they are generally benign.
Causes of Sebaceous Cysts
The formation of sebaceous cysts can be affected by numerous factors. These are:
Blocked Sebaceous Glands
Sebaceous gland blockage or obstruction is the main reason for sebaceous cysts. These glands are in charge of secreting sebum, an oily substance that plays a role in hydrating the hair and skin. A cyst develops when the ducts of these glands block, preventing sebum from hitting the skin’s surface.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal abnormalities can significantly influence sebaceous cyst formation. Teenagers are especially affected by cyst formation during puberty because of hormonal changes that increase sebum production. Similar to this, sebaceous cysts may appear as an outcome of hormonal changes that occur between conception and menopause.
Hair Follicle Damage
Sebaceous cysts can form as a result of harm or trauma to hair follicles. Damage to a hair follicle may prevent sebum from spreading, usually causing an accumulation and cyst formation. This harm may be brought on by causes like rubbing, shaving, or the use of aggressive chemicals.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic predisposition relates to an individual’s hereditary propensity to develop specific characteristics or conditions as an outcome of specific genetic variations passed down from their parents. Genetic factors have been identified as one of the contributing reasons for sebaceous cysts. Although not everyone with a genetic tendency can suffer from sebaceous cysts, specific genetic variations can enhance the likelihood of them occurring.
Skin Conditions and Disorders
Several skin diseases and disorders can increase the possibility of sebaceous cyst production. In some cases, skin can obstruct sebaceous glands, which causes cysts to form. Sebaceous cysts are also more likely to form in individuals who have diseases like hidradenitis suppurativa, a persistent inflammatory skin condition.
Environmental Factors
Sebaceous cysts may appear as an outcome of environmental influences. Cyst formation may be enhanced by damage to certain irritants, chemicals, or substances that interfere with the sebaceous glands’ typical operation. Additionally, extreme heat and humidity can boost sebum production, making people more susceptible to cysts.
Symptoms of Sebaceous Cysts
Now, let’s look at the symptoms of sebaceous cysts:
A lump beneath the skin
Sebaceous cysts usually appear as tiny, rounded lumps under the skin’s surface. These cysts are generally tactile growths that range in size from pea-sized to larger growths. Depending on how the contents are distributed, they could feel firm or slightly squishy. Some cysts grow gradually over time, increasing in size and prominence, while others stay relatively unchanged.
Swelling
People may experience slight swelling or enlargement of the surrounding skin in addition to the cyst itself. The tissue around the cyst may become inflamed or irritated, causing this swelling. If the cyst becomes infected, there’s a chance that the swelling will worsen, and the affected area will get warmer and redder.
Tenderness
Sebaceous cysts can be painful or uncomfortable to the touch, mainly if pressure is applied to the affected area. The cyst’s size, location, and personal pain thresholds can all affect how tender something is. Certain cysts are only slightly uncomfortable, but others can be extremely painful, mainly if they are in places like the back or scalp where pressure is applied frequently.
Sensation of pressure
People who have sebaceous cysts may feel as though something is pressing on or filling up around the cyst. The cyst’s pressure on nearby tissues or organs may be the cause of this sensation. In certain situations, lying down or performing activities that apply pressure to the affected area can make it more apparent.
Rupture and Discharge
There are times when sebaceous cysts burst, and the gross, smelly stuff inside comes out. It may happen on its own or as a result of the cyst being compromised by something like squeezing or puncturing it. Inflammation, infection, and the development of a new cyst can occur when a cyst bursts, although it can also provide an abrupt release of pressure and pain. In order to reduce the possibility of problems from cyst rupture, proper maintenance and care are necessary.
Treatment of Sebaceous Cysts
Now that the causes and symptoms are out of the way let’s explore the different treatment methods available for sebaceous cysts:
Home Remedies
Some people may find relief from sebaceous cyst symptoms by using home remedies. These techniques could include massaging the cyst with tea tree oil, aloe vera gel, or warm compresses to reduce swelling and promote healing. Although they might not be able to solve the problem permanently, home remedies can temporarily relieve symptoms and support medical care.
Conservative Measures
Doctors might advise conservative measures if the sebaceous cyst is small, asymptomatic, and not causing any problems. In order to encourage drainage and lessen inflammation, warm compresses are usually applied to the cyst. It’s also possible to gently press on the cyst to promote natural drainage. Furthermore, infection can be avoided, and the chance of developing new problems can be decreased by keeping the affected area clean.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions are often required if conservative measures are ineffective or if the cyst is causing discomfort or cosmetic concerns. A typical procedure is incision and drainage, in which a medical professional makes a tiny incision in the cyst and removes the contents. Under local anaesthesia, this procedure can be carried out in a clinical setting and offer immediate symptom relief.
Excision Surgery
Surgical excision is sometimes advised for more significant or recurring cysts. With excision surgery, the cyst is surgically removed along with its surrounding capsule in order to stop it from reforming. In most cases, depending on the location and size of the cyst, this procedure is carried out under general or local anaesthesia. A time frame of healing and monitoring may be necessary to ensure appropriate healing after surgery when the wound is typically closed with sutures.
Steroid Injections
In rare cases, doctors may suggest injecting corticosteroids into the cyst to lessen swelling and decrease its size. This course of treatment is typically saved for inflamed or recurring cysts and can help reduce symptoms without requiring surgery. Steroid injections may occasionally need to be administered again to maintain their effectiveness.
Conclusion
Sebaceous cysts, common benign skin growths, can cause discomfort and anxiety. People can effectively manage their conditions and enhance their quality of life by being proactive and learning about their causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. Sebaceous cysts can be effectively treated, and their impact on everyday life can be minimised with the proper care and management.