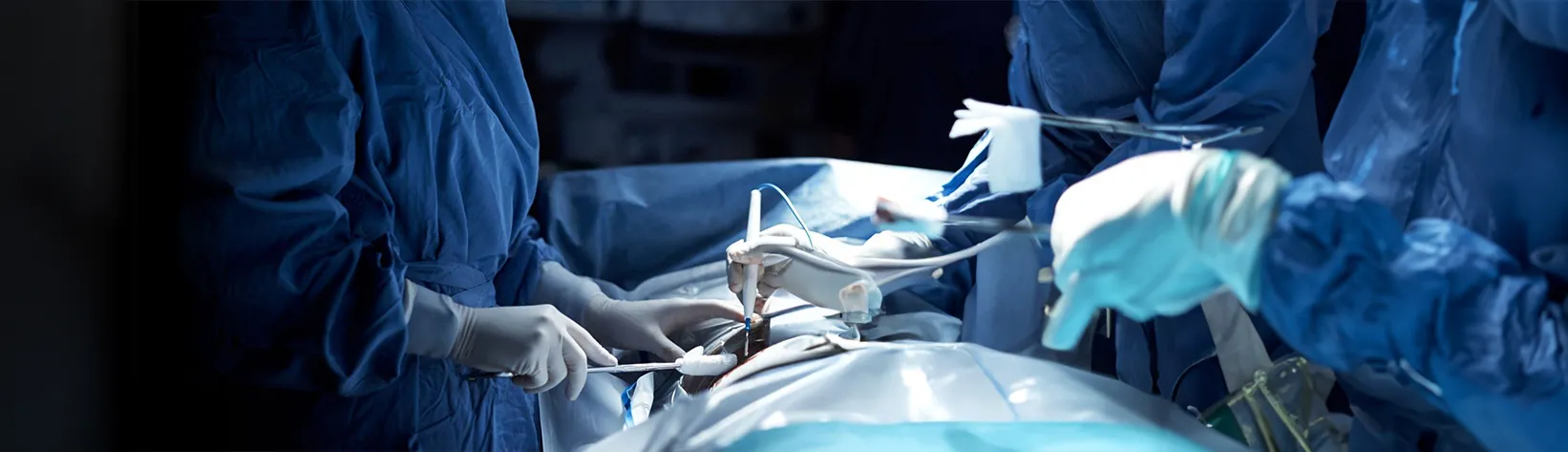
The medical technique known as electrocauterisation surgery, sometimes referred to as electrocautery or thermal cautery, uses heat from a high-frequency electric current to burn, thicken, or cut tissue. This adaptable method is used in a number of medical specialities, such as gynaecology, surgery, and dermatology.
During electro-cauterisation surgery, the targeted tissue is heated to a controlled temperature using a specialised tool called a cautery device. Depending on the goals of the surgery and the medical condition being treated, there are different purposes for this procedure.
What is Electrocauterisation?
Electrocauterisation, also known as cauterisation, is a medical technique in which tissue is treated by means of a high-frequency electric current. The heat produced by this current can be used to close blood vessels effectively, remove tissue growths that aren’t needed, or stop bleeding when performing surgery.
Depending on the strength and length of the electric current, the heat it produces effectively burns or coagulates the tissue. Because electrocauterisation can precisely target and treat specific areas, it is frequently used in a variety of medical specialities, such as gynaecology, surgery, and dermatology.
How Does Electrocauterisation Work?
The process of electrocauterisation involves applying a regulated, high-frequency electric current to the targeted tissue using a specialised tool known as a cautery device. Heat is produced by the electric current flowing through the tissue. Depending on the procedure’s desired result, this heat has multiple uses, including:
Coagulation
The heat produced by electrocautery is sometimes used to clot or coagulate blood vessels. Blocking the blood vessel this helps in preventing the bleeding and promotes hemostasis during surgical procedures.
Tissue Destruction
Tissue can also be burned or evaporated using the electric current’s powerful heat. It is beneficial in the removal of tumours, polyps, and other undesired or abnormal tissue growths.
Precision
The ability of electrocauterisation to precisely target particular tissue areas is one of its main benefits. It makes it possible for medical professionals to carry out delicate operations with little harm to the surrounding healthy tissue.
Purpose of Electrocauterisation Surgery
Electrocauterisation surgery is a valuable medical tool that fulfils multiple purposes.
Hemostasis
Hemostasis, or stopping the bleeding, is one of the main goals of electrocauterisation, especially when performing surgery. This procedure dramatically reduces the possibility of excessive bleeding by precisely sealing blood vessels with a cautery device, which promotes a more precise and controlled surgical environment.
Tissue Removal
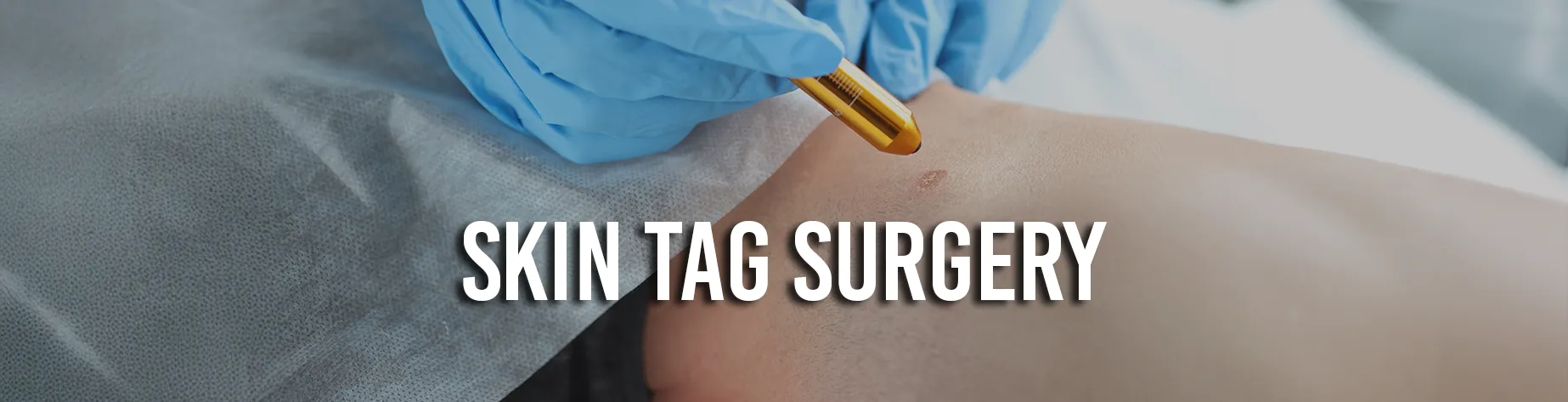
The removal of unwanted or abnormal tissue growths, including skin tags, polyps, and warts, is another critical application for electrocauterisation. With the ability to produce focused heat, the cautery device makes it easier to effectively destroy and then remove the targeted tissue, guaranteeing a systematic and accurate procedure.
Infection Prevention
When wounds or incisions are compromised during surgery, electrocauterisation can play a preventive role in managing infections. With electrocautery, the risk of bacterial contamination and subsequent infection is reduced by effectively sealing the wound edges and creating a protective barrier.
Advantages of Electrocauterisation Surgery
The advantages of electrocauterisation surgery are:
Minimally Invasive Procedure
Due to its reliance on tiny punctures or incisions, electrocauterisation is commonly recognised as a minimally invasive procedure. This distinctive difference from the extensive tissue disruption that comes with open surgery emphasises how careful electrocauterisation is. Electrocauterisation strives to reduce tissue trauma and improve patient outcomes by using a minimally invasive approach.
Achieving surgical goals is made easier and less likely to result in collateral damage to nearby healthy tissue when precise, targeted heat is applied. Patients who undergo electrocauterisation have quicker recovery periods and reduced tissue damage and scarring.
This focus on accuracy and minimally invasive techniques represents a patient-centred approach to surgical care, which promotes effectiveness, comfort, and favourable results.
Reduced Blood Loss
Electrocauterisation surgery is a highly advantageous procedure because of its exceptional capacity to reduce blood loss during the process. The fundamental process of electrocautery, which cauterises blood vessels when cutting tissue, is essential to this ability.
This combined action not only ensures hemostasis but also maintains an unhindered surgical field. It also removes the necessity for blood donations, thereby reducing the risks and complications associated with them.
Electrocauterisationn surgery embodies a commitment to patient safety and optimal surgical outcomes by placing a high priority on hemostasis and surgical precision.
Facilitating Recovery
Electrocauterisation surgery is distinguished not only by its accuracy and effectiveness but also by its capacity to accelerate the healing process. Because of its minimally invasive nature and decreased tissue trauma, patients undergoing electrocauterisation surgery frequently heal more quickly than those undergoing traditional open procedures.
This faster recovery process helps you quickly get back to your regular activities and dramatically reduces the likelihood of complications following surgery. Electrocauterisation surgery is an example of a comprehensive approach to surgical care because it places a high priority on patient comfort, convenience, and recovery. This guarantees not only successful outcomes but also a smooth transition to better well-being.
Electrocauterisation Applications
Electrocauterisation surgery is a collaborative intervention used in many different medical specialities to treat a range of medical conditions. Hemorrhoids, warts, polyps, and skin lesions are among the conditions that electrocauterisation effectively treats.
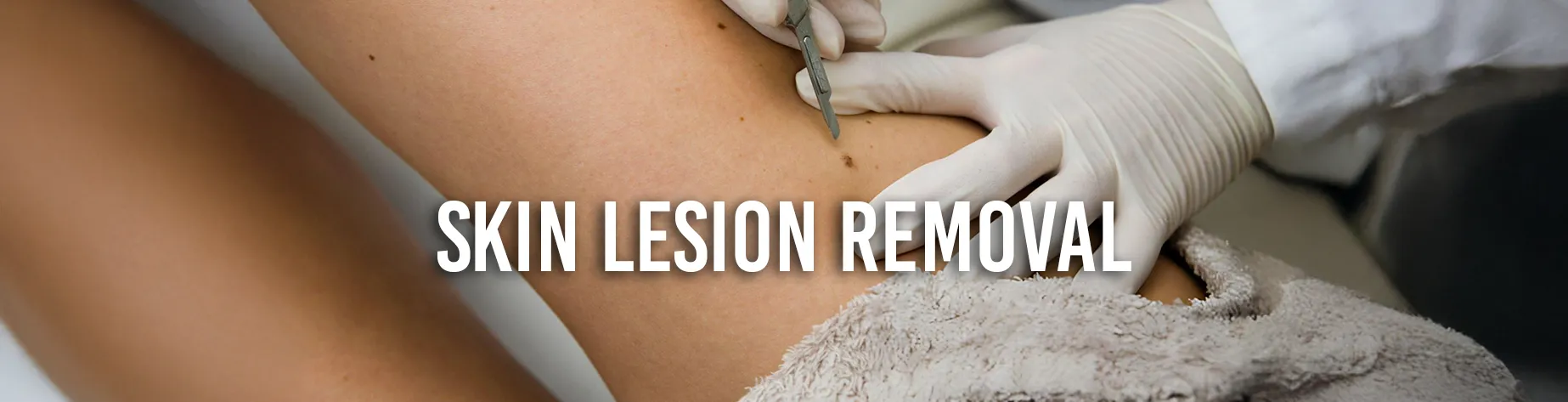
Skin Lesions
Skin lesions are a broad category of abnormalities that include benign growths, skin cancer and precancerous lesions. The precise and efficient removal of these lesions through electrocauterisation promotes both therapeutic efficacy and cosmetic results.
Haemorrhoids
Haemorrhoids are frequently a source of pain and discomfort due to enlarged and irritated veins in the rectum or anus. Hemorrhoidal tissue can be made to coagulate and shrink with electrocauterisation, which relieves symptoms and enhances the quality of life for patients.
Warts
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is the cause of warts, which appear as rough, elevated growths on the skin’s surface. Electrocauterisation destroys afflicted tissue and provides a non-invasive and effective means of treating warts.
Polyps
Polyps are amorphous growths of tissue that can arise in different organs like the stomach, uterus, or colon and can develop into cancer. By precisely removing polyps, electrocauterisation lowers the risk of complications and improves patients’ long-term health.
Conclusion
The medical procedure known as electrocauterisation surgery uses the heat produced by an electric current to treat a wide range of diseases. Electrocauterisationn surgery is the perfect example of a patient-focused approach to healthcare because it places a high priority on and guarantees the best possible results and patient satisfaction.