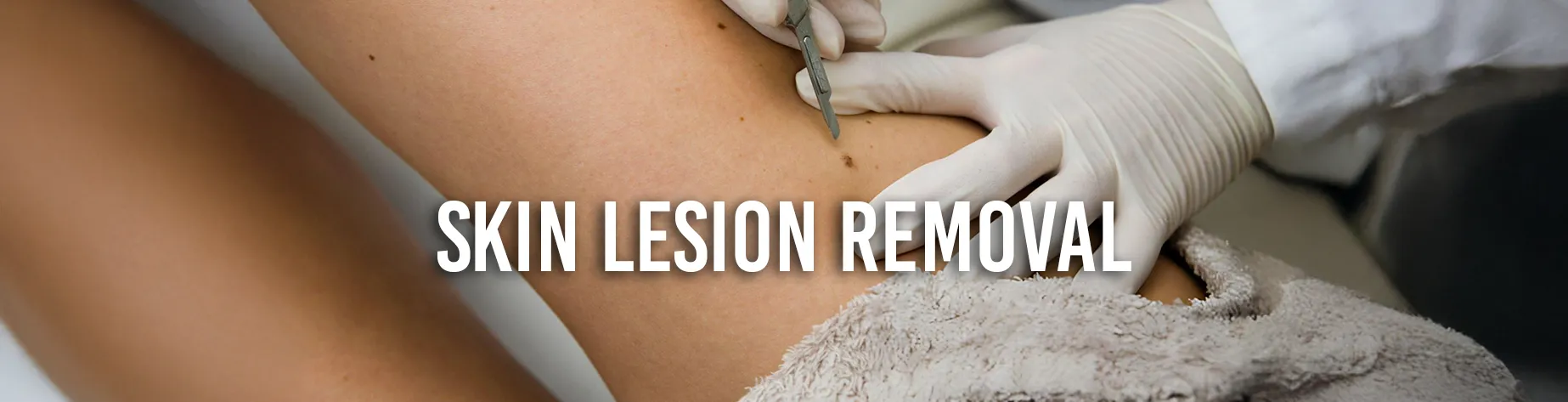
Dermatofibroma is a benign skin growth that can cause problems with a person’s appearance and health. Other non-surgical options are available for treating dermatofibroma, but surgery is the most successful option.
To make well-informed treatment decisions, it’s important to understand what dermatofibromas are, what causes them, and who is the most likely to be affected by them.
In this guide, we will discuss the consequences of the procedure and look into the factors contributing to the acceptance of surgery as the best option for dermatofibroma treatment.
What is dermatofibroma?
Dermatofibromas are common, harmless bumps on the skin that look like raised, brownish dots. Insect bites or other skin injuries can cause them, and they typically appear on the lower legs. Dermatofibromas are not dangerous but may leave a small, visible mark that disappears over time.
Causes of Dermatofibroma
Several factors are believed to contribute to the development of dermatofibroma, though the exact cause of it is not fully understood. These factors include:
Genetics
Dermatofibroma sometimes seems to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. According to genetic research, specific gene mutations can be involved in its development.
Hormonal Fluctuations
Dermatofibroma development may also be influenced by hormonal changes, such as those that take place during puberty or pregnancy. Variations in hormone levels can impact skin growth and the development of cells.
Minor Injury
Dermatofibromas usually occur where there has been prior skin trauma or injury, such as cuts, scratches, or insect bites. It is believed that these minor wounds cause fibrous tissue to grow and eventually result in dermatofibroma. Additionally, inflammatory reactions to trauma could play a role in its development.
Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Dermatofibroma can begin as a result of certain inflammatory skin conditions like ingrown hair or acne. Dermatofibroma can arise as a result of persistent skin inflammation that stimulates the growth of fibrous tissues.
Sun Exposure
Dermatofibroma may also develop as a result of skin cells being damaged by ultraviolet radiation from the sun or having their growth patterns changed. However, there is a need for further research to fully understand the possible correlation between dermatofibroma development and excessive sun exposure, as suggested by some studies.
Symptoms of Dermatofibroma
Dermatofibromas typically appear as small, firm bumps on the skin. They may vary in colour, ranging from pink to brownish-black. These lesions are usually painless but may cause itching or tenderness in some cases. Typically, dermatofibromas measure between 0.5 to 2 centimetres in diameter.
Non-surgical Treatment
It’s important to consider non-surgical options like cortisone injections, cryotherapy, and laser therapy before opting for surgery. These choices might provide some relief but may not work properly at times, resulting in infection, poor healing, and deep scarring from improper removal.
The non-surgical treatment methods are as follows:
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, also called cryosurgery, is a specialised method for removing dermatofibromas by freezing and destroying the infected cells using nitrogen’s cryogenic (freezing) power.
Laser Therapy
Laser Therapy is another non-surgical treatment method that uses concentrated heat to target the hyperproliferation of cells that cause dermatofibromas to grow and persist.
Cortisone Injections
Injections of cortisone work well in reducing dermatofibromas. They also help to relieve the pain and itching that come with dermatofibroma.
Alternative Solution for Treatment
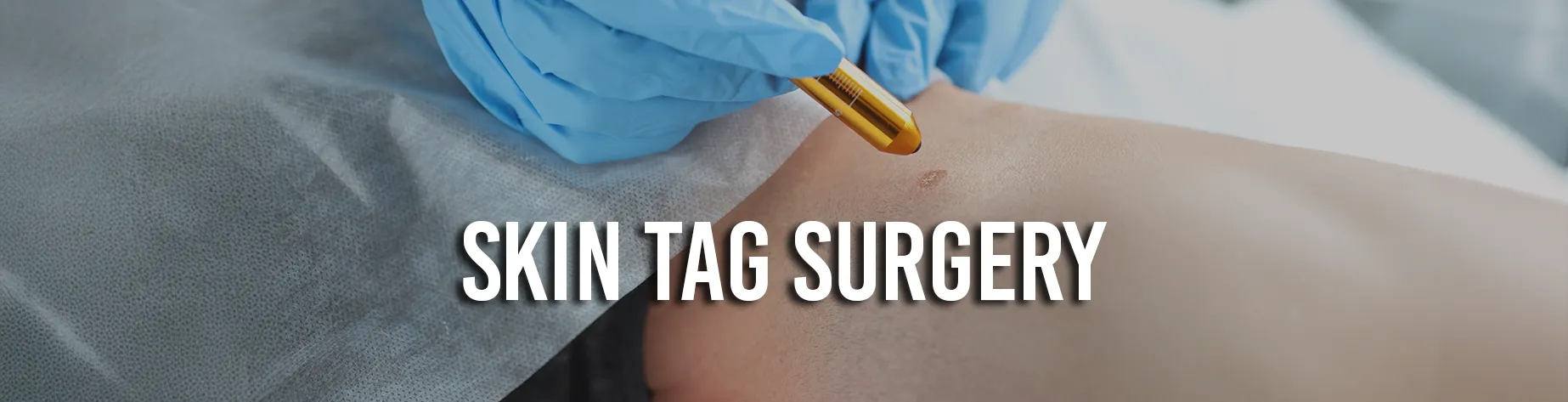
An alternate solution for dermatofibroma is surgical treatment. Dermatofibroma surgery has several benefits. Although surgical removal is the most effective method, there is a chance that the scar will be more noticeable than it was with the original dermatofibroma.
Surgical Removal Procedure
Surgical removal is the most effective and reliable method for removing dermatofibromas. First, local anaesthesia is applied to the desired area to begin the procedure.
The procedure is painless once the anaesthetic takes effect, despite the possibility of slight discomfort during the initial numbing injection. To facilitate optimum healing, the dermatofibroma is carefully removed during surgery, and the skin is meticulously stitched back together.
A dermatologist consultation is necessary before any surgical treatments. Pre-operative instructions and conversations regarding anaesthetic options guarantee a smooth and well-informed treatment.
Types of Surgical Procedures for Dermatofibroma
A few types of surgical procedures for dermatofibroma are:
Excisional Biopsy
With an excisional biopsy, the entire dermatofibroma and an area of benign tissue are surgically removed. It lowers the possibility of a recurrence and guarantees total lesion removal. Following the excision, the tissue is examined under a microscope to verify the diagnosis and guarantee that all abnormal cells have been eliminated.
Shave Excision
Shave excision is a minimally invasive surgical method in which a scalpel or razor blade is used to remove the dermatofibroma’s surface. Although it might not totally remove the lesion, this technique works well for superficial dermatofibromas. Generally speaking, it leaves fewer scars and requires less time to recover from than other surgical procedures.
Punch Biopsy
A punch biopsy involves cutting a small, cylindrical core of tissue containing the dermatofibroma with a circular blade. For smaller lesions, this technique is often used because it facilitates both diagnosis and treatment.
Punch biopsy produces a small but valuable tissue sample that helps guide future management decisions by providing necessary information about the nature of the lesion.
Aftercare of Surgical Removal
As part of the healing process, minor swelling in the treated area is to be expected after the dermatofibroma surgery. For protection, the doctor might apply a dressing; during this initial phase, it’s important to keep everything dry and clean.
Wash your hands with mild soap and water before dealing with the affected area to protect your scar for optimal healing. Use the doctor’s recommended creams and ointments, and this will help ensure that the scars gradually fade over time.
Also, taking some time off from physically demanding activities like heavy lifting or intense exercise is advised. This preventive measure facilitates a quicker healing process.
Conclusion
Dermatofibromas are benign but unwanted, raised scars on the skin that cause cosmetic issues. There are several reasons for their development, but the real causes are yet unknown. Both surgical and non-surgical methods can be used to remove dermatofibromas.
Non-surgical treatments include cryotherapy or laser therapy. These methods are particularly suitable for individuals with smaller dermatofibromas. On the other hand, dermatofibroma surgery remains a widely used and effective approach, especially for larger or deeper lesions. This method ensures complete removal of the dermatofibroma, reducing the likelihood of recurrence, but surgical treatment may involve a longer recovery time and leave a scar.
To determine the most suitable method for dermatofibroma treatment, it is important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional.